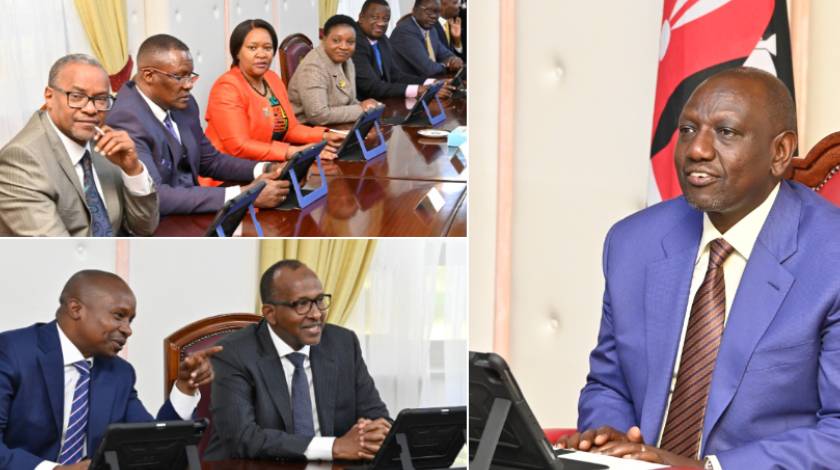
On January 31, the first paperless Cabinet meeting was presided over by President Ruto as the administration begins to digitize its procedures and use technology to increase efficiency.
Over the past ten years, Kenya, like many other nations, has undergone a tremendous digital revolution.
Why Is Government Digitizing Services?
The government is digitizing services for efficiency, openness, and accountability.
Did you read this?

The Kenya Kwanza administration, for instance, is on a journey to promote digitization across all industries, including healthcare, education, agriculture, and finance.
Internet Connection
One of the most visible initiatives under the digitization drive has been the rollout of the National Optic Fibre Backbone Infrastructure (NOFBI) project to connect all county headquarters with high-speed internet.

Former President Kenyatta's government implemented the project in partnership with the private sector.
It has already connected over 30 county headquarters. The connectivity has brought numerous benefits, including improved communication, access to information, and e-government services.
Huduma Center
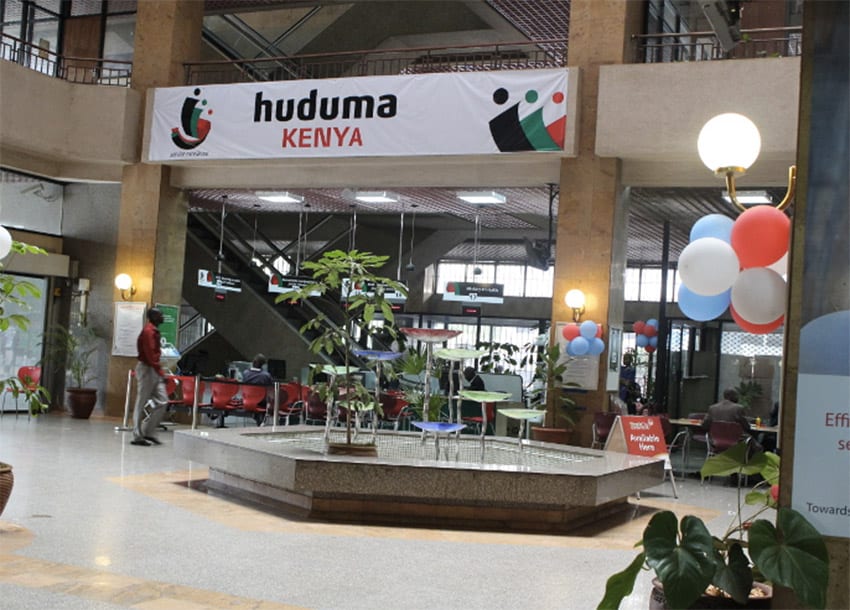
Another key initiative under the digitization drive has been the Huduma Centers. The centre is a one-stop shop for various government services.

Current President William Ruto assured Kenyans of an online Huduma number that will replace the ID number and make service delivery easier.
To improve how quickly Kenyans may access more than 5,000 government services, the Head of State is concentrating on digitizing them.
First-Ever Paperless Meeting
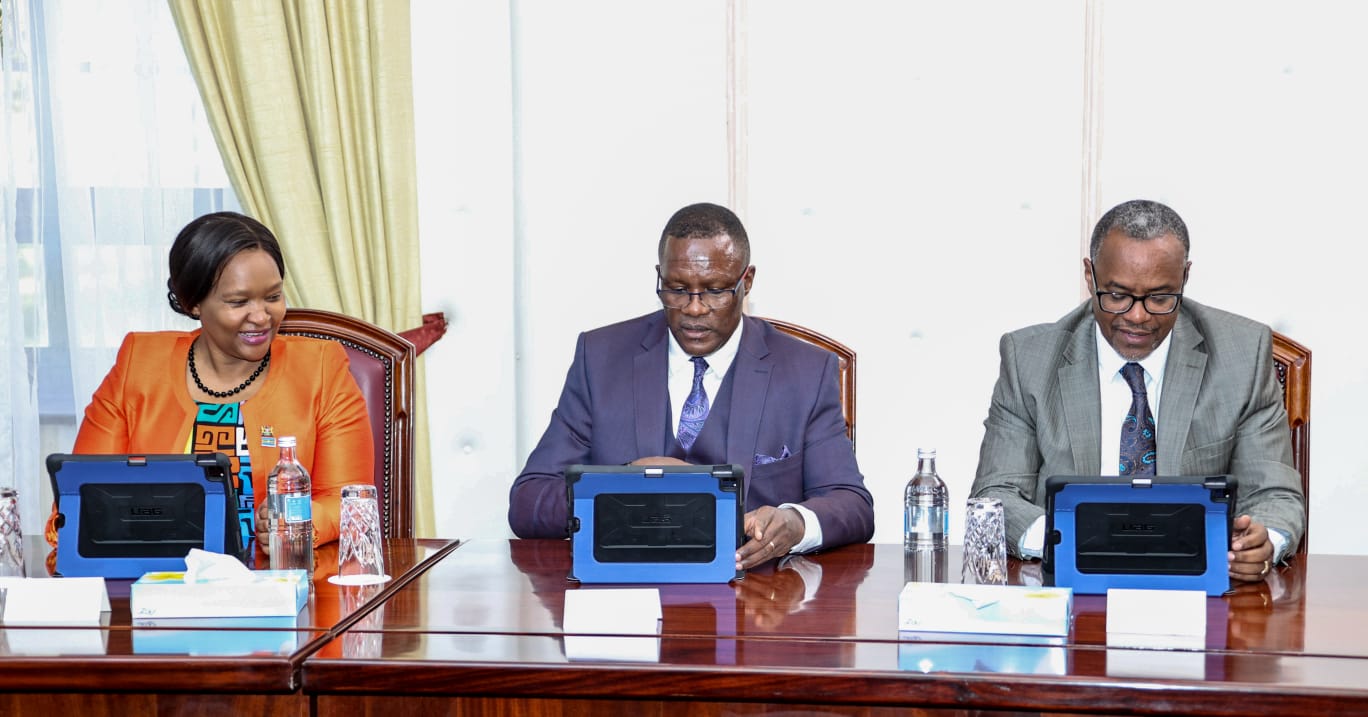
After holding its first paperless meeting at State House on Tuesday, January 31, President William Ruto's Cabinet made the first move toward the government's digitalization program.

During the first-ever paperless meeting, the Presidential Communication Service released images from the Cabinet where the Head of State was engaging in a tablet-related activity.
Kenya Kwanza Administration Top Goal
According to the Kenya Kwanza administration, digitalization of government services is their top goal. They assured Kenyans that they would focus on information exchange, processes, and delivery in particular. The assurance is yet to be confirmed by Kenyans.
Kenya will become more effective, conserve resources, and implement the Plan more quickly, all of which will enhance the people's quality of life in the long run due to digitalization.
President Ruto Said that Kenyans could access government services from their home or offices without having to go unnecessarily to government offices and wait in long queues.
Huduma Center Services
The centres, which the government runs, have been established across the country and provide services such as identity cards, birth and death certificates, business registration, and tax services, among others. The Huduma Centers have greatly improved service delivery, reducing the time and cost of accessing government services and enhancing efficiency in the process.
Education Sector
In the education sector, the government has been pushing for the digitization of the curriculum, focusing on e-learning and the provision of digital devices to learners.
Government's Digital Literacy Programme(DLP)
The government's Digital Literacy Programme (DLP) aims to provide all Class One pupils in public primary schools with digital devices, such as tablets, loaded with educational content.
Pupils Who Have Benefited From DLP Programme
This program has already benefited over 1 million pupils and has greatly enhanced access to quality education, particularly in remote and marginalized areas.
What Is The Government Working On In The Health Sector?
The government has been pushing for the digitization of health records to improve service delivery, reduce costs, and enhance access to healthcare.

- E-Health Strategy
The government's e-Health strategy seeks to provide a comprehensive electronic health record system, which will allow for the sharing of patient information across different healthcare facilities, thereby reducing duplication of services and improving patient outcomes. The digitization of health records has also led to improved monitoring of disease outbreaks and the tracking of health trends and patterns.
Agriculture Sector
The government has promoted mobile technology and digital platforms to enhance access to markets, information, and finance.

- E-Voucher
One of the key initiatives in the agriculture sector has been the e-Voucher system. The system provides farmers with subsidies for inputs such as seeds and fertilizers. The agriculture ministry under CS Mithika Linturi is currently using this initiative to distribute fertilizers.
The system has greatly improved access to agricultural inputs and increased productivity and incomes for farmers.
Finance Sector
The government has been promoting digital platforms to enhance access to financial services, particularly for the unbanked and underbanked populations.
- Government's National Payment System (NPS)
The government's National Payment System (NPS) seeks to provide a modern and efficient payment system that will allow for the seamless and secure transfer of funds across different platforms. The government has also been promoting mobile money platforms, such as M-Pesa, to enhance financial inclusion, particularly in rural areas.
Despite the many benefits of digitization, the government has faced several challenges in its implementation. One of the key challenges has been the need for adequate infrastructure, particularly in remote and marginalized areas. It has led to uneven access to digital services, with many people still needing access to essential services such as internet connectivity.