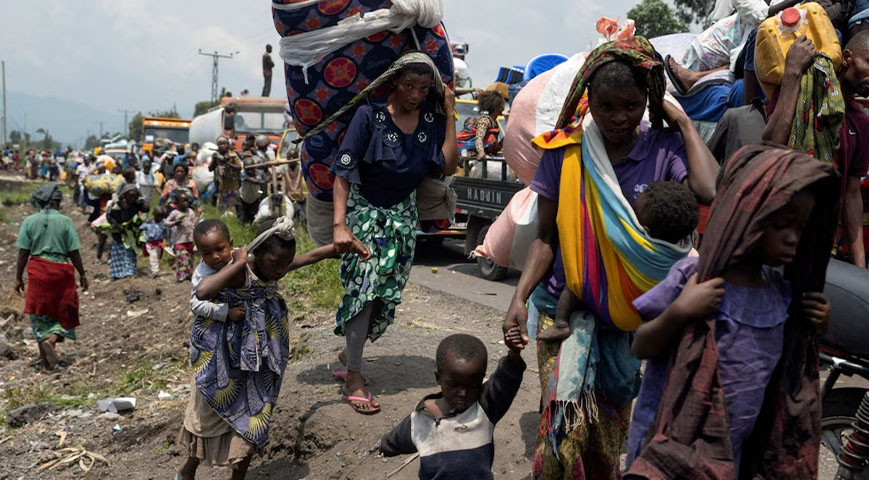
Immigration and emigration are two terms that are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings. Immigration involves the movement of individuals or groups of people from one country to another with the intention of settling permanently.
Emigration, on the other hand, refers to the act of leaving one's own country to live permanently in another country. In this article, we will discuss the differences between immigration and emigration.
Immigration is a process that involves a person or a group of people leaving their country of origin and moving to another country with the intention of staying there permanently. People immigrate for various reasons, such as seeking better economic opportunities, better education, and better living conditions. Immigration can occur legally, through government programs such as work visas, student visas, and permanent residency, or illegally, through unauthorized border crossings or overstaying visas.
Immigrants usually face a range of challenges when they arrive in their new country. These challenges include cultural and language barriers, adapting to a new way of life, finding employment, and adjusting to the different legal and political systems. Nonetheless, immigrants often bring new skills, knowledge, and perspectives that contribute positively to the economy and society of their host country.
Emigration, on the other hand, involves leaving one's own country to live permanently in another country. People emigrate for various reasons, such as political instability, social unrest, persecution, and economic hardship. Emigration can be voluntary or forced, such as in the case of refugees fleeing conflict or persecution in their home country.
Emigrants also face a range of challenges when they arrive in their new country. These challenges include adapting to a new culture and language, finding employment, and navigating a new legal and political system. In addition, emigrants often experience homesickness and a sense of disconnection from their cultural roots.
One of the main differences between immigration and emigration is the direction of the movement. Immigration involves moving to a new country, while emigration involves leaving one's home country. Another key difference is

Immigration can be voluntary or forced. Voluntary immigration occurs when people choose to leave their home country for various reasons, including seeking better economic opportunities, education, political stability, or religious freedom. Forced immigration, on the other hand, occurs when people are forced to leave their home country due to political persecution, war, or natural disasters.
Immigrants often face various challenges as they adjust to a new culture and society. They may experience language barriers, discrimination, or difficulties in finding employment or affordable housing. However, immigration can also bring many benefits, including economic growth, cultural diversity, and innovation.
Emigration, on the other hand, often involves leaving one's home country due to economic or social factors such as poverty, unemployment, or political instability. Emigrants may also seek better opportunities, education, or healthcare in other countries. However, emigration can also be a result of forced displacement due to war or persecution.
Emigrants may face various challenges as they leave their home country, such as leaving behind family, friends, and familiar surroundings. They may also face challenges in adapting to a new culture, language, and society. However, emigration can also bring benefits, such as remittances sent back to the home country, which can help to support the local economy.
There are various reasons why people choose to immigrate or emigrate. One of the most common reasons is to seek better economic opportunities. People may move to other countries to find work that pays better or offers better benefits. They may also move to countries with lower living costs or better social services.
Immigration and emigration can also be influenced by political factors. For example, people may leave their home country due to political persecution, war, or the violation of their human rights. They may also move to countries that are more politically stable or offer better protection for their basic rights.
Cultural factors can also influence immigration and emigration. People may move to other countries to learn new languages, experience different cultures, or seek out new opportunities for personal growth. They may also leave their home country due to cultural conflicts or the desire to live in a more diverse and inclusive society.
The impact of immigration and emigration can vary depending on the country of origin and the country of destination. Immigration can bring benefits such as economic growth, cultural diversity, and innovation. However, it can also lead to challenges such as social tensions and cultural clashes. Emigration can lead to economic growth in the home country through remittances but can also lead to brain drain, which can affect the economy and social services.
In conclusion, immigration and emigration are two terms that are often used interchangeably, but they have different meanings. Immigration refers to the movement of people from one country to another with the intention of settling permanently, while emigration refers to the act of leaving one's own country to live permanently in another country. Understanding the difference between these two terms is important as it helps to differentiate the experiences and challenges that come with each. Immigration and emigration can bring benefits and challenges to both the countries of origin and destination, making them significant factors that have shaped the world today.