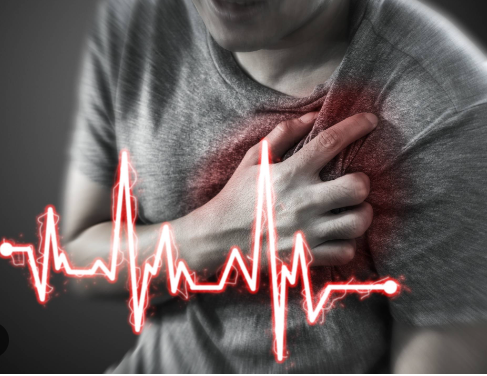
Cardiac arrest is a medical emergency that occurs when the heart suddenly stops beating. It is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention. The signs and symptoms of cardiac arrest can vary, but some common ones include the following:
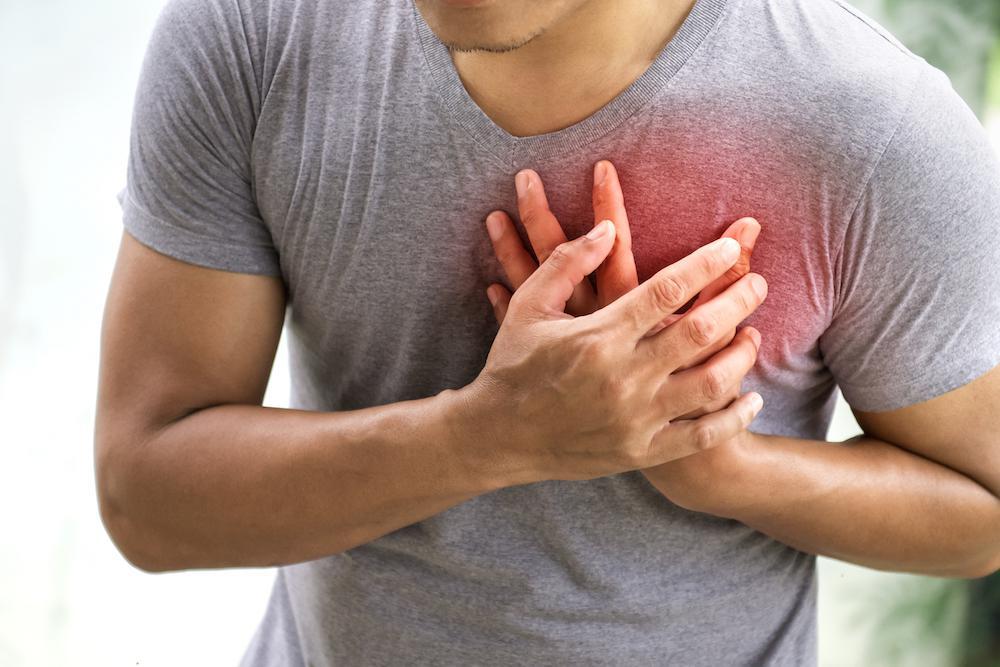

Sudden loss of consciousness: A person experiencing cardiac arrest will suddenly lose consciousness and will not respond to any stimuli.
Did you read this?
No pulse: A person experiencing cardiac arrest will not have a pulse, and their skin may appear pale or blue.
No breathing: A person experiencing cardiac arrest will not be breathing or gasping for breath.
Chest pain: Some people may experience chest pain or discomfort before or during cardiac arrest.
Shortness of breath: Some people may experience shortness or difficulty breathing before or during cardiac arrest.
Fatigue or weakness: Some people may experience fatigue or weakness before or during cardiac arrest.
Dizziness or lightheadedness: Some people may experience dizziness or lightheadedness before or during cardiac arrest.
Nausea or vomiting: Some people may experience nausea or vomiting before or during cardiac arrest.
Sweating: Some people may experience sweating before or during cardiac arrest.
It is crucial to note that not all people experiencing cardiac arrest will have all of these signs and symptoms. Additionally, some people may have cardiac arrest without experiencing any symptoms.
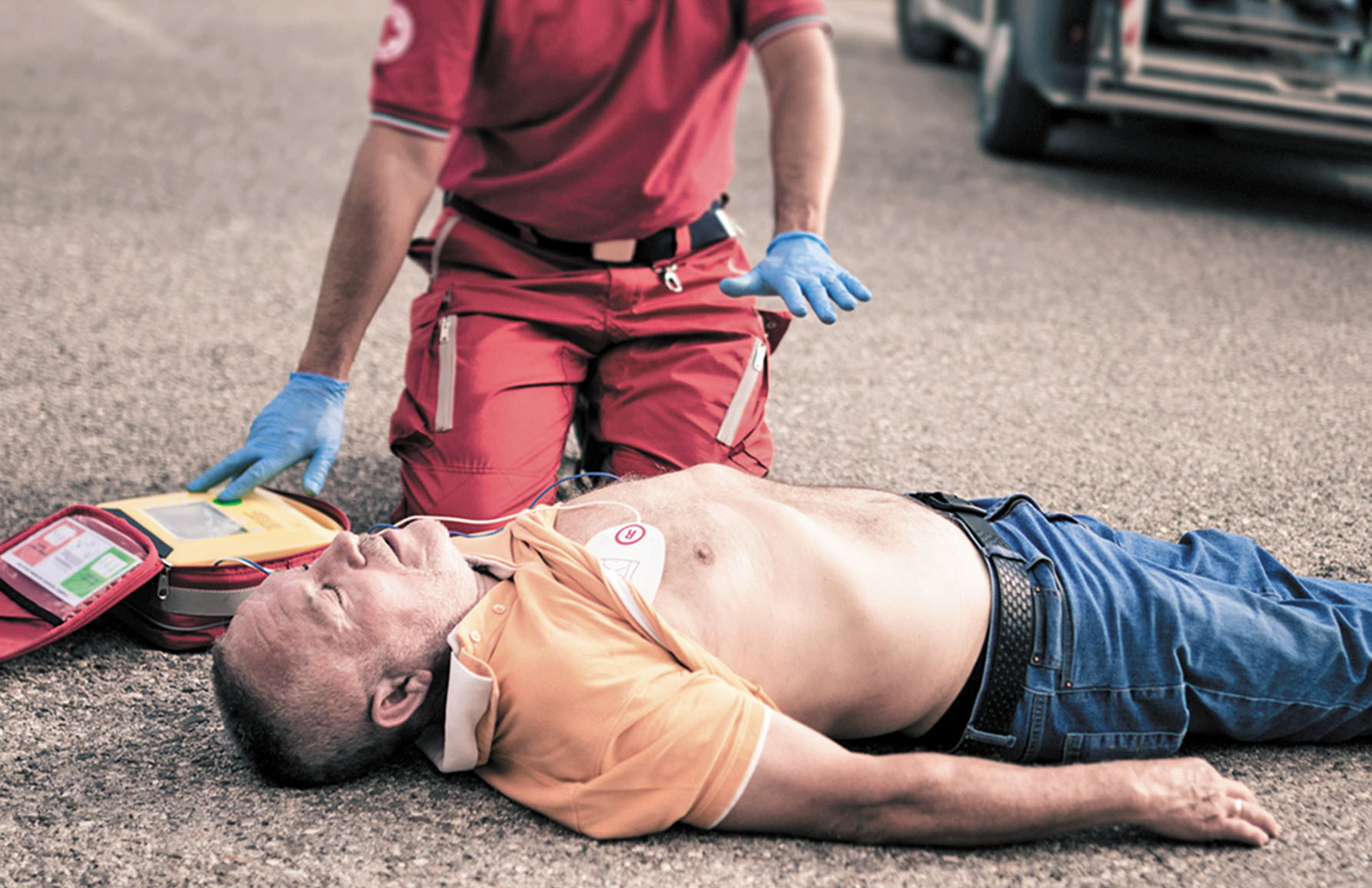
If you feel like someone is experiencing cardiac arrest, call the helpline immediately and begin CPR if you are trained to do so. Early intervention and treatment can significantly improve an individual's chances of survival after a cardiac arrest.
It is also essential to distinguish between cardiac arrest and a heart attack. A heart attack is a circulation problem in which blood flow to the heart is blocked or reduced. If the damage to the heart is severe enough, a heart attack can result in cardiac arrest.