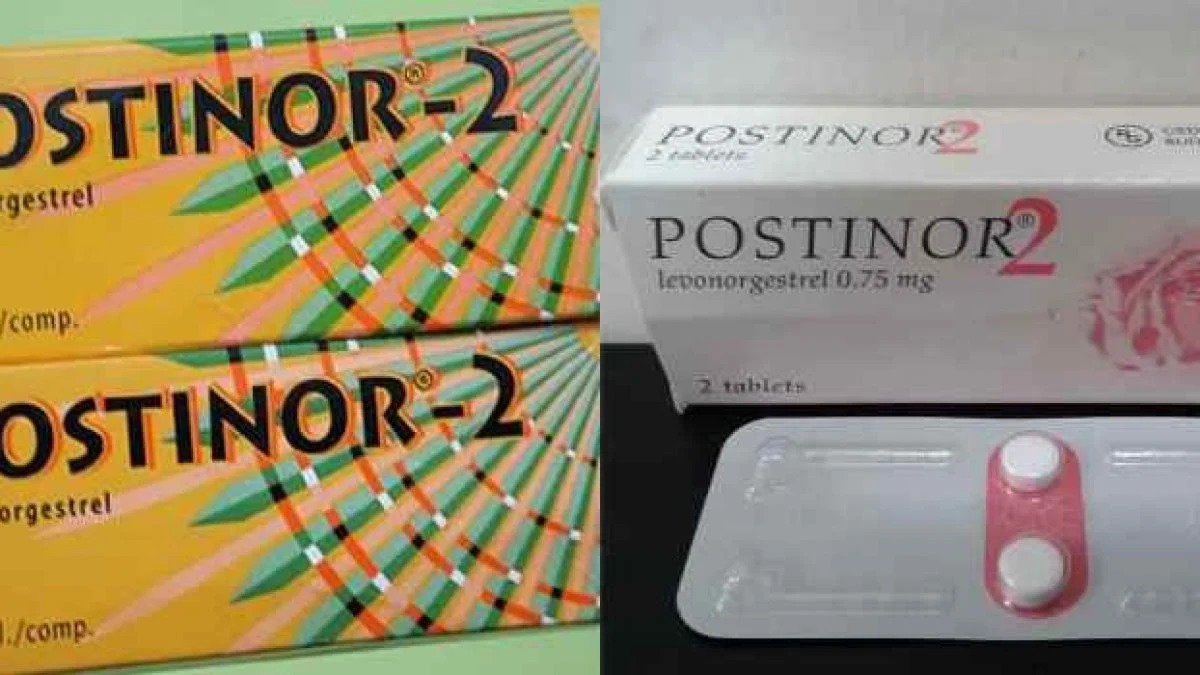
Sexual liberation and changing relationship ideas have made young people more open-minded and curious about their sexual life. Research shows that more women are turning to using Postinor-2 as a contraception.
While this increasing independence has undoubtedly brought about favourable developments, it has also resulted in unforeseen effects, such as the misapplication of contraceptive pills.

With the increased availability and accessibility of contraception, particularly oral contraceptive tablets, young people now have more control over their reproductive health and the opportunity to engage in sexual activities without fear of pregnancy.
This ease of access, however, has resulted in a casual and occasionally irresponsible attitude toward contraceptive pill use.
According to the Kenya Demographic and Health Survey, 70% of sexually active unmarried women aged 15-49 use contraception, with 59% using a contemporary technique.

Traditional methods are used more frequently by sexually active single women than currently married women (11% vs. 6%, respectively).
Injectables (20%), implants (19%), and contraceptive pills are the most often utilized techniques among currently married women.
In addition to Postinor-2, other contraceptive tablets are available. Knowing that each contraceptive pill has a unique hormonal formulation, dose, and usage instructions is vital. Combination Pills, progestin-only Pills (Mini Pills), and prolonged Cycle Pills Emergency are some contraceptive pills.
These pills, like Postinor-2, are designed to be used following unprotected intercourse or contraceptive failure. They include larger hormone doses and work best when taken as soon as possible after intercourse. Plan B One-Step, Next Choice, and Ella are among the more emergency contraceptive pills.
In recent years, many young individuals in Kenya have used Postinor-2, which costs only Ksh.100 to Ksh.150 in most Kenyan pharmacies.
This development has raised worries among healthcare professionals, parents, and the general public. Misuse of Postinor-2 poses serious health hazards and raises concerns about a lack of comprehensive sexual education and cheap contraception techniques.
Several reasons contribute to the increasing misuse of Postinor-2, including restricted access to proper sexual education. Many young people are unaware of contraception techniques and how to use them correctly.