Research shows that cats can get AIDS, too, but the one that affects them differs from the one that affects humans. Feline immunodeficiency virus FIV is an infectious disease that affects cats worldwide.
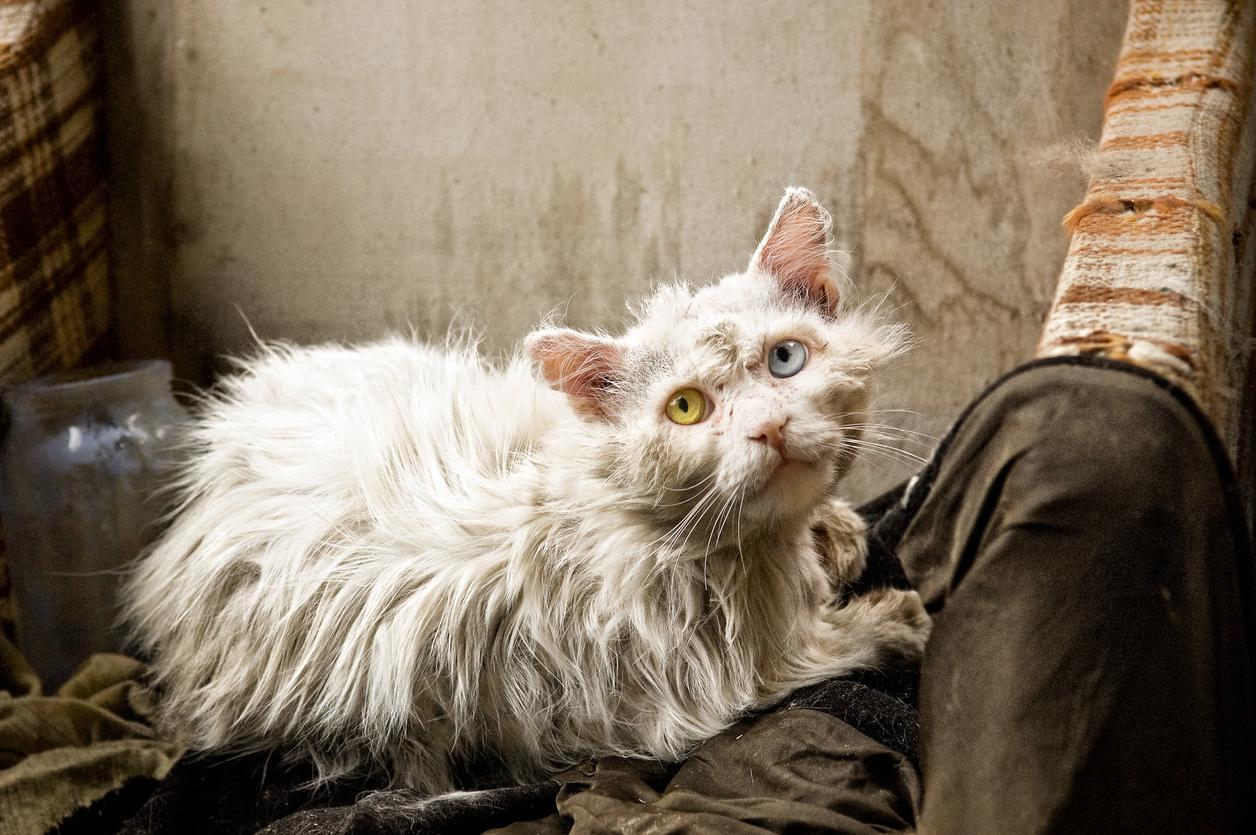

The feline immunodeficiency virus functions similarly to HIV in attacking the cat's immune system, leaving it vulnerable to opportunistic diseases. Although there is no cure for FIV, cats with the condition live a long life if they do not develop the feline leukaemia virus.
No, it cannot be transmitted to humans as it is species-specific, so it can only transmit between cats, at least for now.
Did you read this?
FIV spreads through bite wounds from an infected cat. Household cats are not at risk of infection because they rarely fight for resources.on rare occasions, the mother can transmit FIV to her kittens. The risk of infection is, however, higher when the mother gets infected with FIV during her pregnancy.
Unlike humans, sexual contact does not play a significant role in the spread of infection among cats. North America has the most feline immunodeficiency virus cases. FIV infection affects approximately 2.5-5% of healthy cats.
The feline immunodeficiency virus progresses through three stages: acute, asymptomatic (or latent), and progressive. Generally, the acute phase of infection generally occurs 1-3 months after infection.
Cats will then enter an asymptomatic phase that can last months to years. At this stage, the virus replicates very slowly within immune system cells. There are no warning signs yet. Cats will then enter a progressive immunocompromised state, during which secondary infections are possible. Most FIV-related illness is caused by secondary infections or immune system problems rather than the virus itself.
After reaching this stage, the cat usually has only a few months to live.









