Cardiac arrest is a life-threatening medical condition when the heart suddenly stops beating. Various factors can cause cardiac arrests, such as heart disease, heart attack, or trauma. In order to avoid cardiac arrest, it is critical to maintain a healthy lifestyle and manage any underlying medical conditions that might trigger cardiac arrest.
1. Eat a healthy diet
One of the most efficient strategies for avoiding cardiac arrest is to eat a healthy diet. A low-fat, low-cholesterol diet can help lower the likelihood of heart disease and stroke. Vitamin-rich foods like fruits, veggies, and whole grains can also help lower blood pressure and cholesterol.
2. Watch your weight
Did you read this?
Another way of preventing cardiac arrest is watching your weight. Being obese and overweight increases the risk of heart disease, leading leads to cardiac arrest. Weight loss is a great way to stay fit and maintain good health.

3. Work out frequently
it is important to exercise so that you can be fit. Exercise is very is also essential in preventing cardiac arrest. Regular physical activity of at least 45 minutes a day can help lower blood pressure, improve circulation, and maintain a healthy weight—cardio-based activities such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
4. avoid smoking cigarettes.
People who smoke cigarettes are at a higher risk of getting cardiac arrest. Smoking cigarettes daily can harm the heart and blood vessels, leading to an increased likelihood of a heart attack or cardiac arrest. The best way to minimize your risk is to quit smoking.

5. Controlling any underlying medical conditions
Controlling any underlying conditions that one may have can also aid in preventing cardiac arrest. The patient must work with their healthcare provider to manage these conditions when the individual has high cholesterol. Make sure you take your medication on time and observe other health recommendations.
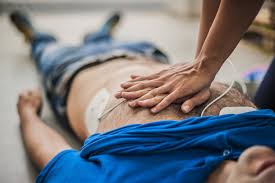
Finally, It is also critical to recognize cardiac arrest symptoms, such as rapid deterioration, no heart rate, no breathing, and lack of responsiveness, and to act quickly if these symptoms occur. This act could include dialling an emergency line and trying to perform CPR until help arrives.